

Ku' Ike
Frequently Asked Questions
| Question 1 What are scabies? Question 2 |
Answer Question 1 Courtesy Dr. Derek Ching: Scabies (SKAY-bees) What is scabies? Scabies is an infestation of the skin by a tiny mite. This is a common problem that affects people of all races and social classes. Scabies spreads rapidly under crowded conditions where there is frequent skin-to-skin contact between people, such as in hospitals, institutions, child-care facilities. 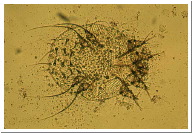 Scabies mite through a microscope What are the signs and symptoms of
scabies infestation? How did I get scabies? How long will mites live? Did my pet spread scabies to me? How is scabies infestation diagnosed? Can scabies be treated? Who should be treated for scabies? Question 2
Courtesy Dr. Derek Ching: Who is at risk for getting head lice? Anyone who comes in close contact with someone with ‘ukus, contaminated clothing, and other belongings. Most common in preschool and elementary-age children (3-10 y.o.), and their families. Girls get ‘ukus more often than boys. What do head lice look like? There are three forms of lice: the nit, the nymph, and the adult. Nit: Nits are head lice eggs. They are hard to see and often confused for dandruff or hair spray droplets. They are oval and usually yellow to white. Nits take about 1 week to hatch. Nymph: The nit hatches into a nymph. It takes about 7 days for nymphs to mature into adults. Nymphs must feed on blood to survive. Adult: Size of a sesame seed, six legs, and is tan to greyish-white. In persons with dark hair, the adult will look darker. Females lay nits; they are usually larger than males. Like scabies, can live up to one month on a person, but dies in 2 days if falls off. Where are ‘ukus most commonly found? On the scalp behind the ears and near the neckline at the back of the neck. ‘Ukus hold on to hair with hook-like claws at the end of their legs. ‘Ukus are rarely found on the body, eyelashes, or eyebrows. What are the signs and symptoms of ‘uku infestation? • Tickling, irritating feeling of something moving in the hair. • Itching, caused by an allergic reaction to the bites. • Sores on the head caused by scratching. These sores can sometimes become infected. How did my child get ‘ukus? • By contact with an already infested person. Contact is common during play at school and at home (slumber parties, sports activities, at camp, on a playground). • By wearing infested clothing, such as hats, scarves, coats, sports uniforms, or hair ribbons. • By using infested combs, brushes, or towels. • By lying on a bed, couch, pillow, carpet, or stuffed animal that has recently been in contact with an infested person. How is ‘uku infestation diagnosed? By looking closely through the hair and scalp for eggs or moving ‘ukus. This can be hard because there are usually few of them and they can move quickly from searching fingers. If you are not sure have a professional take a look. How is it treated? • Permethrin (1%) cream placed on the scalp for 10 minutes. Repeat in one week. Works for 2 weeks. No prescription needed. • Pyrethrin-based products: 10 minute shampoos. No prescription needed. Repeat in 1 week. Don’t use if person is allergic to chrysanthemums. • Lindane (1%) 4 minute shampoo that requires a prescription for people that still have ‘ukus after the other treatments have failed. Repeat in 1 week. Do not use in people who have seizures, premature infants, in pregnant or nursing women. • Malathion (0.5%) Requires a prescription. 8-12 hour applied to head and repeated in 1 week. • Do not have to remove dead ‘ukus after treatment • Check other family members or close contacts. • Usually not allowed in school until treated. Return to top of page
|