
Network Driver Installation for Windows 3.1
(How to install TCP/IP on a PC running Windows 3.1)
Level of expertise: Easy..........Intermediate..........Hard
Always backup your data prior to making any configuration changes. ITS is not
responsible for loss of data.
This procedure requires some technical knowledge as it changes the network settings. If a
computer person is available, please consult with him or her before proceeding.
ITS has standardized on the 3com Ethernet 10baseT network cards. If using another
network card, use the appropriate drivers. ITS has also purchased a site license for the
University community to use Trumpet Winsock. Should you decide to follow these
instructions using our standard configuration, it is assumed that you are a UH faculty,
staff, or student. Please click on the following links to download the necessary software
for your installation needs, then save each file on a separate floppy diskette:
- Trumpet Winsock
3com packet driver
Follow these steps to install the network driver in a PC running Windows 3.x:
Installation of Trumpet Winsock:
- Windows 3.1 should already be on your desktop before installing the Network Interface
Card (NIC).
- Power off your computer; install the NIC and connect it to the network cable.
(Check your manuals for installation of adapter cards.)
- Restart your computer.
- After Windows has restarted, insert the diskette that contains Trumpet Winsock
in your floppy drive.
- Double-click on the FILE MANAGER icon inside the MAIN program group in
Program Manager.
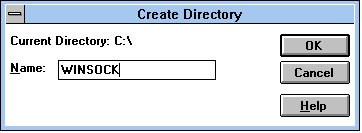
- Use your mouse to click on the C directory.

- Click on FILE, and select Create Directory.
- Type C:\WINSOCK on the command line, and click OK.
- When the previous steps are finished, press F8 on your keyboard, and type in to
the lines as shown below:

- Click on the C drive button, and find the directory C:\WINSOCK.
- On the right-hand column, you should see the file trum21f.exe.
- Double-click on that file, a new window should pop up and show the extraction of the
file that you clicked on. Go ahead and close that new window after it stops moving.
- Go back to PROGRAM MANAGER, open the STARTUP program group.
- Click on FILE, NEW, and select NEW PROGRAM FILE option.
- In the new window, click on the BROWSE button, locate the file C:\WINSOCK\TCPMAN.EXE,
and click OK.
- A new icon in the STARTUP group should appear.
Installation of NIC Packet Driver:
- Insert the diskette that contains the file: 3c509x.com in your floppy disk drive.
- While your are still in FILE MANAGER, press the F8 key.
- Type A:\*.* in the "From" line and C:\ in the "To"
line.
- Go back to PROGRAM MANAGER, select FILE, then RUN.
- On the new command line, type SYSEDIT.
- Find the window that contains AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
- Add the following two lines into the file before WIN, which that word usually
locates in the very bottom of the file:

- Save the changes to the file and exit Windows. Then reboot computer by pressing Ctrl-Alt-Delete
at the same time.
- After Windows restarts, hold down the ALT key while press the TAB key
until you reach the TCPMAN window.
- Click on FILE, SETUP.
- Enter your designated IP, DNS, and subnet mask numbers in the appropriate rows, and
click OK.
In most case your IP will be similar to 128.171.xxx.xxx; gateway will be 128.171.xxx.1;
DNS will be 128.171.3.13 and 128.171.1.1; and subnet mask will be 255.255.255.0; contact
ITS if unsure.
For the DNS entry, type in the two sets of numbers in the following format:
128.171.3.13 (space) 128.171.1.1
- Click OK again to close the warning message.
- Exit the Winsock program by pressing Alt-F4 at the same time, or click on FILE
-> EXIT.
- In PROGRAM MANAGER, go to the STARTUP program group, and double click on
the Winsock icon.
- Winsock should display your IP number. If the number is different from the one you
entered, you might have a duplicate copy of Winsock.
- Minimize
but DO NOT close the Winsock program. The minimize button is located at the
upper right-hand corner, and has a symbol of a triangular arrow pointing downward.
- Test your network connection by running an internet application e.g. telnet or Eudora.
Maintained by:
PC-Help |
Copyright © 1999 University of Hawaii
Last Reviewed: March 9, 2001 |





